Asked by Araceli ArredondoLona on Jun 11, 2024

Verified
Merriwell Corporation has a virtual monopoly in the ultra-high speed computer market. Merriwell has recently introduced a new computer that will be used by satellite installations around the world. The installations have identical demands for the computers. Merriwell's managers have decided to lease rather than sell the computer, but they have been unable to decide whether to use a single hourly rental charge or a two-part tariff. Under the two-part tariff, users would be levied an "access charge" plus an hourly rental rate. Merriwell's marketing staff estimates the demand and marginal revenue curves below for each potential user:
P = 45 - 0.025Q
MR = 45 - 0.05Q,
where P = price per hour of computer time, and Q = the number of hours of computer time leased per month. Merriwell offers their users extensive maintenance assistance and technical support. The firm's engineers estimate that marginal cost is $30 per computer hour.
a. Assuming that Merriwell chooses to set a single price, what are the firm's profit maximizing price and output?
b. Assuming that Merriwell uses a two-part tariff, what "access charge" and hourly rental fee should the firm set? Compare the firm's revenues under the options in (a) and (b).
c. Briefly describe how differing demand curves among the various buyers would alter the two-part tariff.
Two-part Tariff
A two-part tariff is a pricing strategy involving a fixed fee plus a variable usage rate, commonly used in utilities and services to cover both fixed and variable costs.
Access Charge
An access charge is a fee paid by telecommunications companies to use the network infrastructure of another company.
Hourly Rental Rate
The charge applied for renting a service or product by the hour.
- Acquire knowledge of the two-part tariff concept and its deployment in various cases.
- Ascertain optimal rates and charges through evaluation of market demand and variable cost.

Verified Answer
45 - 0.05Q = 30
-0.05Q = -15
Q = 300
P = 45 - 0.025(300)
P = 45 - 7.5
P = 37.50
TR = 37.50 × 300 = $11,250
b.Under a two-part tariff with identical consumers, price and output are determined where P = Mc.45 - 0.025Q = 30
-0.025Q = -15
Q = 600
P = 45 - 0.025(600)
P = 30
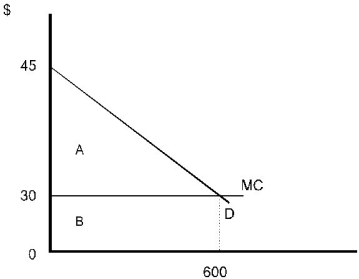 To find access charge, must find the consumer surplus which is area a.Area A = CS = (0.5)(15)(600) = 4,500
To find access charge, must find the consumer surplus which is area a.Area A = CS = (0.5)(15)(600) = 4,500Set access charge of $4,500 and a $30 hourly fee.Total revenue under this option is the area under demand curve or $22,500. Total revenue doubles with a two-part tariff as compared with the single hourly rental charge option.
c.With differing demands, the firm should set prices slightly above MC. The access charge should then be set to capture all consumer surplus from the buyer with the smallest demand.

Learning Objectives
- Acquire knowledge of the two-part tariff concept and its deployment in various cases.
- Ascertain optimal rates and charges through evaluation of market demand and variable cost.
Related questions
A Firm Setting a Two-Part Tariff with Only One Customer ...
Suppose That 1,000 People Are Interested in Attending ElvisLand ...
Suppose That 2,500 People Are Interested in Attending ElvisLand ...
Suppose That 3,500 People Are Interested in Attending ElvisLand ...
A Monopolist Faces the Inverse Demand Curve P ...