Asked by Camille James on May 02, 2024

Verified
Although their formulas are similar, one primary difference between a z-score (z) and a t-statistic (t) is that the ______ of the formula for the t-statistic involves ______.
A) denominator; the variability of individual scores (Xs) , not the variability of sample means 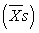
B) numerator; difference between a score (X) and a population mean (μ)
C) denominator; the variability of sample means 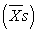 , not the variability of individual scores (Xs)
, not the variability of individual scores (Xs)
D) numerator; the difference between a score (X) and a sample mean 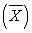
T-statistic
A statistic used in hypothesis testing, computed as the difference between the sample mean and the hypothesized population mean, divided by the standard error of the mean.
Z-score
A statistical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values, measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean.
Variability
The extent to which data points in a statistical distribution or data set diverge from the average or mean value.
- Become familiar with the differences that exist between z-scores and t-statistics.

Verified Answer
SS
Shiri ShaheidMay 08, 2024
Final Answer :
C
Explanation :
The denominator of the formula for the t-statistic involves the variability of sample means, not the variability of individual scores (Xs) as in the z-score formula. This is because the t-statistic is used when we do not know the population standard deviation, and therefore need to estimate it using the sample standard deviation, which introduces additional variability into the calculation. The numerator of the t-statistic formula still involves the difference between a score (X) and a sample mean, as in the z-score formula.

Learning Objectives
- Become familiar with the differences that exist between z-scores and t-statistics.