Asked by christie xiong on Jul 16, 2024

Verified
For a particular gene, the frequency of the dominant allele H is 0.65. The total population size is 10,000 individuals. In addition, the homozygous recessive condition results in living but sterile offspring. Fill in the table of values for the generations indicated:
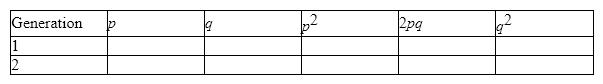 Does this population exhibit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Why or why not? If not, what assumptions does the Hardy-Weinberg principle make that appear to be inapplicable in this situation?
Does this population exhibit Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Why or why not? If not, what assumptions does the Hardy-Weinberg principle make that appear to be inapplicable in this situation?
Dominant Allele
An allele that expresses its phenotype even in the presence of another (recessive) allele.
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
A principle stating that genetic variation in a population will remain constant from one generation to the next in the absence of disturbing factors.
Homozygous Recessive
An individual that has inherited two identical alleles for a particular trait from each parent, manifesting a trait that is only expressed when dominant alleles are absent.
- Comprehend the core principles of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and the particular conditions necessary for its application.
- Analyze factors affecting allele frequencies and understand the concept of genetic equilibrium.

Verified Answer
MP
Maria PatinoJul 20, 2024
Final Answer :
Concepts to Consider: The Hardy-Weinberg equation allows students to calculate the value for q (0.35) based on the frequency of H (= p ). The values for the particular genotypes are then processed mathematically (the last three columns of the table for generation 1 are 4,225 individuals; 4,550 individuals; 1,225 individuals). The values of p and q in the second generation are based on the fact that the individuals with the recessive genotype ( q 2) are sterile and are therefore removed from the reproductive population. The number of alleles in the population equals the number of surviving offspring × 2, or 17,610. Of these, 13,060 are dominant H alleles (the number of homozygous dominant individuals × 2 + the number of heterozygous individuals) and 4,550 are recessive h alleles. This allows for the calculation of new values for p (0.74) and q (0.26) with associated changes in the number of individuals with each genotype.

Learning Objectives
- Comprehend the core principles of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and the particular conditions necessary for its application.
- Analyze factors affecting allele frequencies and understand the concept of genetic equilibrium.