Asked by Adeeb Ebaad on Apr 25, 2024

Verified
The market demand for a type of carpet known as KS-12 has been estimated as
P = 75 - 1.5Q,
where P is price ($/yard), and Q is output per time period (thousands of yards per month). The market supply is expressed as P = 25 + 0.50Q. A typical competitive firm that markets this type of carpet has a marginal cost of production of
MC = 2.5 + 10q.
a. Determine the market equilibrium price for this type of carpet. Also determine the production rate in the market.
b. Determine how much the typical firm will produce per week at the equilibrium price.
c. If all firms had the same cost structure, how many firms would compete at the equilibrium price computed in (a) above?
d. Determine the producer surplus the typical firm has under the conditions described above. (Hint: Note that the marginal cost function is linear.)
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service demanded equals the quantity supplied, resulting in market balance.
Marginal Cost
The added total cost resulting from the manufacture of one more unit.
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good versus what they actually receive, often represented as the area above the supply curve and below the equilibrium price.
- Calculate the market equilibrium output, output per firm, and the resulting profit or loss in a competitive market setting.

Verified Answer
50 = 2Q
Q = 25 (thousand yards per month)
The equilibrium selling price is
P = 75 - 1.5(25) = $37.5/yard.b.Since the firm's supply is based on its MC curve, we can use MC to determine production rate.P = 37.5 = MC = 2.5 + 10q
q =
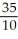 = 3.5 (thousand yards / month)
= 3.5 (thousand yards / month)c.Since each firm produces 3.5 thousand yards per month and total production is at 25 thousand yards per month, a total of 7.14 firms would be needed.d.Producer surplus is the area between the price of $37.5 and MC, bounded by zero and 3.5 units of output for the typical firm. The bounded area is a triangle.Area =
 b ∙ h = (0.5)(3.5)(37.5 - 2.5) = $61.25 (thousand)
b ∙ h = (0.5)(3.5)(37.5 - 2.5) = $61.25 (thousand)
Learning Objectives
- Calculate the market equilibrium output, output per firm, and the resulting profit or loss in a competitive market setting.
Related questions
The Market for Wheat Consists of 500 Identical Firms, Each ...
The Market Demand for a Type of Carpet Known as ...
Assume the Market for Tortillas Is Perfectly Competitive ...
(Table: Pumpkin Market)There Are Two Consumers,Andy and Ben,in the Market ...
(Table: Pumpkin Market)There Are Two Consumers,Andy and Ben,in the Market ...