Asked by Chukwuebuka Mochaauchefuna on Apr 26, 2024

Verified
The standard error of the sampling distribution of sample proportion, SE ( 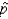 ), depends on the value of the population proportion p, and the closer the value of p to .50, the larger SE (
), depends on the value of the population proportion p, and the closer the value of p to .50, the larger SE ( 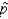 ) will be for a given sample size n.
) will be for a given sample size n.
Standard Error
Standard error measures the accuracy with which a sample distribution represents a population by quantifying the variability of the sample mean.
Population Proportion
The fraction or percentage of a population possessing a particular characteristic.
Sample Size
The number of observations or units chosen from a population to participate in a study.
- Ascertain the critical role of the Central Limit Theorem in the control of statistical processes.
- Acquire insight into how the calculation of control limits is affected by the standard error of the sample proportion.

Verified Answer
CB
Corinne BrownApr 30, 2024
Final Answer :
True
Explanation :
This statement is true. When the population proportion is closer to .50, the distribution is more spread out and thus the standard error of the sample proportion will be larger for a given sample size compared to when the population proportion is further away from .50. This is because there is more uncertainty in estimating the population proportion when it is close to .50.

Learning Objectives
- Ascertain the critical role of the Central Limit Theorem in the control of statistical processes.
- Acquire insight into how the calculation of control limits is affected by the standard error of the sample proportion.
Related questions
The Central Limit Theorem States That When the Sample Size ...
A Normal Distribution Is Generally Described by Its Two Parameters ...
The Central Limit Theorem ...
The Data Below Represent the Means from 15 Sample Control ...
Sample Proportions That Are ____________________ Than the Lower Control Limit ...