Asked by Veronica Lovtsova on Jun 01, 2024

Verified
The Tire Shed is a regional chain that sells tires and other automobile parts. The company sells its own brand of tires under a block pricing scheme that charges $100 per tire if the customer buys one or two tires and $75 per tire if the customer buys three or four tires. The monthly demand curve facing the typical store is Q = 1000 - 4P, and the marginal cost of the tires is constant at $40 per tire.
a. What are the monthly profits for the typical store under the block pricing scheme? What is the consumer surplus enjoyed by customers of the typical store?
b. Suppose the firm is considering a uniform pricing scheme with P = $90 per tire. How does the firm profit and consumer surplus under uniform pricing compare to the profit and consumer surplus outcomes under block pricing?
Block Pricing Scheme
A pricing strategy where different quantities of a product or service are sold at different prices, typically decreasing with volume.
Marginal Cost
The increased cost resulting from the production of an extra unit of a product or service.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between the total amount consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service and the total amount they actually pay.
- Ascertain the most effective pricing policies for monopolists engaging in discriminatory pricing across theoretical frameworks and applied cases.

Verified Answer
ZK
Zybrea KnightJun 04, 2024
Final Answer :
a.The firm sells Q1 = 1000 - 4(100) = 600 tires at the high price (P1 = 100), and the firm's profit from the first block is 600(100 - 40) = $36,000. The demand curve may be stated in price-dependent form as P = 250 - 0.25Q, and the consumer surplus under the first block is 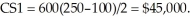 At the lower price, Q2 = 1000 - 4(75) = 700 (i.e., the typical Tire Shed sells 100 tires per month under the second block), the firm's profit under this block is
At the lower price, Q2 = 1000 - 4(75) = 700 (i.e., the typical Tire Shed sells 100 tires per month under the second block), the firm's profit under this block is 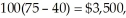 and the total profit is $39,500 per month. The consumer surplus under the second block is CS2 = 100(100 - 75)/2 = $1,250, and the aggregate consumer surplus is $46,250 per month.b.Under the uniform pricing scheme with P = $90, the quantity demanded is
and the total profit is $39,500 per month. The consumer surplus under the second block is CS2 = 100(100 - 75)/2 = $1,250, and the aggregate consumer surplus is $46,250 per month.b.Under the uniform pricing scheme with P = $90, the quantity demanded is 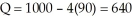 tires per month, and the firm's profit is
tires per month, and the firm's profit is 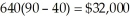 per month. The consumer surplus under the uniform pricing scheme is
per month. The consumer surplus under the uniform pricing scheme is 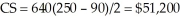 per month. As expected, the firm profits are higher and the consumer surplus is lower under the block pricing scheme.
per month. As expected, the firm profits are higher and the consumer surplus is lower under the block pricing scheme.
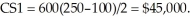 At the lower price, Q2 = 1000 - 4(75) = 700 (i.e., the typical Tire Shed sells 100 tires per month under the second block), the firm's profit under this block is
At the lower price, Q2 = 1000 - 4(75) = 700 (i.e., the typical Tire Shed sells 100 tires per month under the second block), the firm's profit under this block is 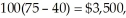 and the total profit is $39,500 per month. The consumer surplus under the second block is CS2 = 100(100 - 75)/2 = $1,250, and the aggregate consumer surplus is $46,250 per month.b.Under the uniform pricing scheme with P = $90, the quantity demanded is
and the total profit is $39,500 per month. The consumer surplus under the second block is CS2 = 100(100 - 75)/2 = $1,250, and the aggregate consumer surplus is $46,250 per month.b.Under the uniform pricing scheme with P = $90, the quantity demanded is 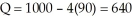 tires per month, and the firm's profit is
tires per month, and the firm's profit is 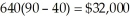 per month. The consumer surplus under the uniform pricing scheme is
per month. The consumer surplus under the uniform pricing scheme is 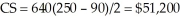 per month. As expected, the firm profits are higher and the consumer surplus is lower under the block pricing scheme.
per month. As expected, the firm profits are higher and the consumer surplus is lower under the block pricing scheme.
Learning Objectives
- Ascertain the most effective pricing policies for monopolists engaging in discriminatory pricing across theoretical frameworks and applied cases.