DE
Daphne Espinoza Gonzalez
Answers (6)
DE
Answered
Martha is looking for work as a electrical engineer. Her prospects are good but so far she has not taken a job. Jennifer is looking for work in a paper mill. Every time Jennifer shows up for an interview, there are more people looking for work than there are openings. She realizes that it has been that way for a long time.
A) Martha and Jennifer are both frictionally unemployed.
B) Martha and Jennifer are both structurally unemployed.
C) Martha is frictionally unemployed, and Jennifer is structurally unemployed.
D) Martha is structurally unemployed, and Jennifer is frictionally unemployed.
A) Martha and Jennifer are both frictionally unemployed.
B) Martha and Jennifer are both structurally unemployed.
C) Martha is frictionally unemployed, and Jennifer is structurally unemployed.
D) Martha is structurally unemployed, and Jennifer is frictionally unemployed.
On Jul 25, 2024
C
DE
Answered
More and more, U.S. laws are becoming increasingly based on the rule of caveat emptor: "Let the buyer beware."
On Jul 22, 2024
False
DE
Answered
The insurer would likely attempt to deny coverage based on which of the following legal theories?
A) Negligence
B) Recklessness
C) Breach of contract
D) Misrepresentation
E) Illegality
A) Negligence
B) Recklessness
C) Breach of contract
D) Misrepresentation
E) Illegality
On Jun 23, 2024
C
DE
Answered
Premiums for whole-life insurance are generally smaller than those for term-life insurance.
On Jun 20, 2024
False
DE
Answered
Andrew's neighbor,Charles,is selling drugs from his home.Since Andrew is concerned about the well-being of his own family,he offers to pay Charles $60,000 to stop selling drugs.Charles stops,but Andrew refuses to pay.Can Charles successfully sue Andrew to force him to pay the $60,000? Explain.
On May 24, 2024
No,a party cannot make valid consideration out of a promise to stop doing something that was illegal to do in the first place.
DE
Answered
Howell Corporation's activity-based costing system has three activity cost pools--Machining, Setting Up, and Other. The company's overhead costs, which consist of equipment depreciation and indirect labor, are allocated to the cost pools in proportion to the activity cost pools' consumption of resources.
 Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools
Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools
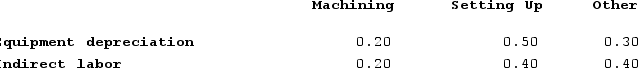 Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products.
Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products.
 Additional data concerning the company's products appears below:
Additional data concerning the company's products appears below:
 Required:a. Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools using activity-based costing.b. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing.c. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing.d. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing.
Required:a. Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools using activity-based costing.b. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing.c. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing.d. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing.
 Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools
Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools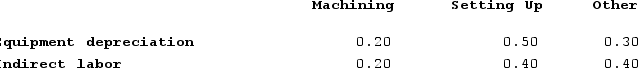 Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products.
Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products. Additional data concerning the company's products appears below:
Additional data concerning the company's products appears below: Required:a. Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools using activity-based costing.b. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing.c. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing.d. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing.
Required:a. Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools using activity-based costing.b. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing.c. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing.d. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing.On May 21, 2024
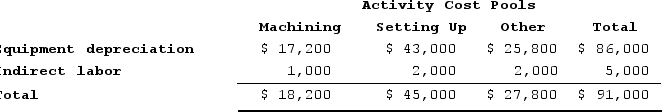
a.Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools by applying the percentages in the Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools table to the respective costs. For example, the first entry in the table is computed as follows: 0.20 × $86,000 = $17,200.
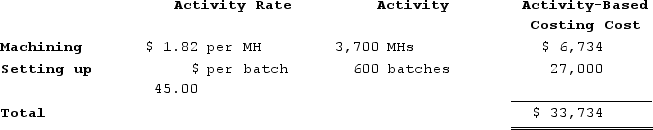
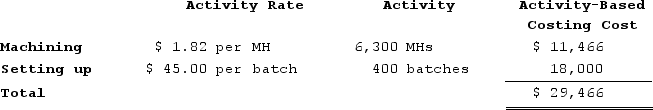
 b.Computation of activity rates:
b.Computation of activity rates:
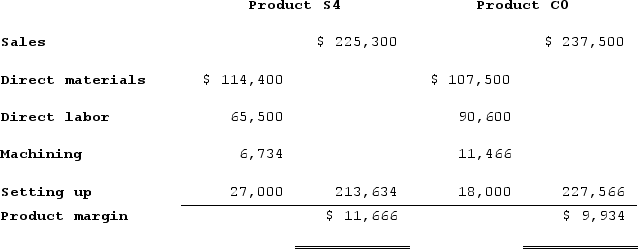
 c.Assign overhead costs to products:Overhead cost for Product S4:
c.Assign overhead costs to products:Overhead cost for Product S4:
 Overhead cost for Product C0:
Overhead cost for Product C0:
 d.Determine product margins:
d.Determine product margins:
 b.Computation of activity rates:
b.Computation of activity rates: c.Assign overhead costs to products:Overhead cost for Product S4:
c.Assign overhead costs to products:Overhead cost for Product S4: Overhead cost for Product C0:
Overhead cost for Product C0: d.Determine product margins:
d.Determine product margins: