JH
Julia Hannah
Answers (6)
JH
Answered
Group culture does not include
A) Values
B) Beliefs
C) Customs
D) Status
A) Values
B) Beliefs
C) Customs
D) Status
On Jul 12, 2024
D
JH
Answered
Reference groups include only family members whom we have grown up with and trust.
On Jul 11, 2024
False
JH
Answered
A fair insurance policy is one in which the premium equals the expected value of the claim.
On Jun 12, 2024
True
JH
Answered
State three major reasons why people immigrate to the United States.
On Jun 11, 2024
People immigrate into the United States legally or illegally to (1)take advantage of superior economic opportunities, (2)escape political or religious oppression, (3)to reunite with family members or other loved ones, usually prior immigrants, who are already in the United States.
JH
Answered
Suppose an oligopolistic producer assumes its rivals will ignore a price increase but match a price cut.In this case the firm perceives its:
A) demand curve as being of unit elasticity throughout.
B) supply curve as kinked,being steeper below the going price than above.
C) demand curve as kinked,being steeper below the going price than above.
D) demand curve as kinked,being steeper above the going price than below.
A) demand curve as being of unit elasticity throughout.
B) supply curve as kinked,being steeper below the going price than above.
C) demand curve as kinked,being steeper below the going price than above.
D) demand curve as kinked,being steeper above the going price than below.
On May 13, 2024
C
JH
Answered
Sarah and Jane are two representative individuals living in an economy that produces two goods, X and Y. Sarah's and Jane's utility functions are given as:
Sarah: US = 100X0.5Y0.5
Jane: UJ = 50X0.4Y0.6
The market determined prices of X and Y are $10 and $20, respectively. Current outputs are 58 units of X per time period and 36 units of Y. Jane's current income is $600 per time period, while Sarah's income is $700 per time period.
a. Write expressions for Sarah and Jane's marginal rates of substitution.
b. Determine the quantities of X and Y that Sarah and Jane should consume in equilibrium.
c. Do the values calculated in part (b) satisfy the conditions for equilibrium in exchange? Explain using numbers.
d. Examine your answers in parts (b) and (c). If equilibrium has not been achieved, what would be necessary to reach equilibrium? If equilibrium has been achieved, comment on the process by which equilibrium was reached.
Sarah: US = 100X0.5Y0.5
Jane: UJ = 50X0.4Y0.6
The market determined prices of X and Y are $10 and $20, respectively. Current outputs are 58 units of X per time period and 36 units of Y. Jane's current income is $600 per time period, while Sarah's income is $700 per time period.
a. Write expressions for Sarah and Jane's marginal rates of substitution.
b. Determine the quantities of X and Y that Sarah and Jane should consume in equilibrium.
c. Do the values calculated in part (b) satisfy the conditions for equilibrium in exchange? Explain using numbers.
d. Examine your answers in parts (b) and (c). If equilibrium has not been achieved, what would be necessary to reach equilibrium? If equilibrium has been achieved, comment on the process by which equilibrium was reached.
On May 11, 2024
a.Jane's MRS: 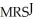 =
= 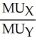 =
= 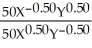 =
= 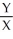 Sarah's MRS:
Sarah's MRS: 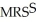 =
= 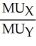 =
= 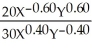 =
= 
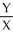 b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to
b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to 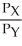 .
. 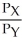 =
= 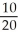 =
=  For Jane:
For Jane: 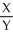 =
=  , Y =
, Y =  X
X
For Sarah:
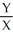 =
=  ,
, 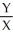 =
=  ∙
∙  Y =
Y =  X
X
To determine quantities substitute into each individuals budget constraint.
Jane's budget constraint: 600 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (1/2)X
600 = 10X + 20(1/2)X
600 = 10X + 10X
X = 30
600 = 10(30) + 20Y
300 = 20Y
Y = 15
Jane should consume 30 units of X and 15 units of Y.
Sarah's budget constraint: 700 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (3/4)X
700 = 10X + 20(3/4)X
700 = 25X
X = 28
700 = 10(28) + 20Y
420 = 20Y
Y = 21
Sarah should consume 28 units of X and 21 units of Y.
c.In equilibrium MRSJ should equal MRSS.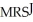 =
=  Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X.
Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X. 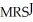 =
= 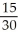 =
= 
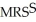 =
=  X
X
Sarah is consuming 21 units of Y and 28 units of X.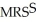 =
= 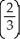
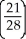 =
= 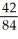 =
= 
 does equal
does equal 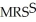 , and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.
, and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.
d.Equilibrium has been achieved. The equilibrium involves an equilibrium in resource markets determining Jane's and Sarah's incomes, in the product market allocating L and K between X and Y, and the condition for efficiency in output that matches production to Jane and Sarah's preferences.
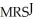 =
= 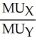 =
= 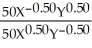 =
= 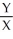 Sarah's MRS:
Sarah's MRS: 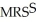 =
= 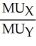 =
= 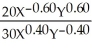 =
= 
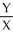 b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to
b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to 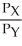 .
. 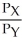 =
= 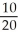 =
=  For Jane:
For Jane: 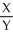 =
=  , Y =
, Y =  X
XFor Sarah:

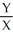 =
=  ,
, 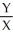 =
=  ∙
∙  Y =
Y =  X
XTo determine quantities substitute into each individuals budget constraint.
Jane's budget constraint: 600 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (1/2)X
600 = 10X + 20(1/2)X
600 = 10X + 10X
X = 30
600 = 10(30) + 20Y
300 = 20Y
Y = 15
Jane should consume 30 units of X and 15 units of Y.
Sarah's budget constraint: 700 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (3/4)X
700 = 10X + 20(3/4)X
700 = 25X
X = 28
700 = 10(28) + 20Y
420 = 20Y
Y = 21
Sarah should consume 28 units of X and 21 units of Y.
c.In equilibrium MRSJ should equal MRSS.
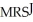 =
= 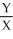 Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X.
Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X. 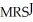 =
= 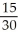 =
= 
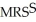 =
=  X
XSarah is consuming 21 units of Y and 28 units of X.
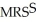 =
= 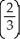
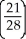 =
= 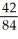 =
= 
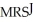 does equal
does equal 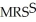 , and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.
, and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.d.Equilibrium has been achieved. The equilibrium involves an equilibrium in resource markets determining Jane's and Sarah's incomes, in the product market allocating L and K between X and Y, and the condition for efficiency in output that matches production to Jane and Sarah's preferences.