MF
Marcus Fielder
Answers (6)
MF
Answered
Based on the Accenture survey on sources of risk that affect global supply chain performance,which of the following was found to have affected the highest percentage of supply chains?
A) shortage of skilled resources
B) volatility of fuel prices
C) inflexible supply chain technology
D) customs delays
A) shortage of skilled resources
B) volatility of fuel prices
C) inflexible supply chain technology
D) customs delays
On Jul 25, 2024
B
MF
Answered
A pure discount loan is defined as a loan where a borrower receives money today in exchange for:
A) Annual interest payments and the repayment of the principal at the end of the loan period.
B) Increasing loan payments over the life of the loan.
C) Equal loan payments over the life of the loan.
D) Equal loan payments for a period of time followed by one large payment at the end of the loan term.
E) One lump sum payment at the end of the loan term.
A) Annual interest payments and the repayment of the principal at the end of the loan period.
B) Increasing loan payments over the life of the loan.
C) Equal loan payments over the life of the loan.
D) Equal loan payments for a period of time followed by one large payment at the end of the loan term.
E) One lump sum payment at the end of the loan term.
On Jul 21, 2024
E
MF
Answered
Assuming fixed costs remain constant,and a company produces more units than it sells,then income under absorption costing is less than income under variable costing.
On Jun 25, 2024
False
MF
Answered
Successful strategies share several essential features. Which of the following is NOT one of these essential features?
A) Every strategy requires leaders who are willing to take risks on behalf of the organisation.
B) Every strategy requires supporting structures, well-designed tasks and workflows, and the right people.
C) Every strategy requires leaders who can energise people and build performance commitments.
D) The entire organisation and all of its resources must be mobilised in support of the strategies.
E) Every strategy requires leaders who can use teams and teamwork to the best advantage.
A) Every strategy requires leaders who are willing to take risks on behalf of the organisation.
B) Every strategy requires supporting structures, well-designed tasks and workflows, and the right people.
C) Every strategy requires leaders who can energise people and build performance commitments.
D) The entire organisation and all of its resources must be mobilised in support of the strategies.
E) Every strategy requires leaders who can use teams and teamwork to the best advantage.
On Jun 21, 2024
A
MF
Answered
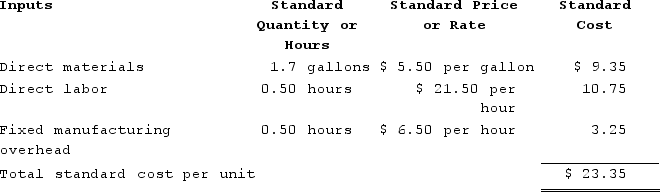
Zaino Corporation manufactures one product. It does not maintain any beginning or ending Work in Process inventories. The company uses a standard cost system in which inventories are recorded at their standard costs and any variances are closed directly to Cost of Goods Sold. There is no variable manufacturing overhead. The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
 The company calculated the following variances for the year:
The company calculated the following variances for the year:
 The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $48,750 and budgeted activity of 7,500 hours.
The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $48,750 and budgeted activity of 7,500 hours.
During the year, the company completed the following transactions:
a. Purchased 45,600 gallons of raw material at a price of $4.90 per gallon.b. Used 40,220 gallons of the raw material to produce 23,600 units of work in process.c. Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 12,400 hours at an average cost of $21.70 per hour.d. Applied fixed overhead to the 23,600 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $34,050. Of this total, −$23,950 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $58,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment.e. Transferred 23,600 units from work in process to finished goods.f. Sold for cash 23,700 units to customers at a price of $27.20 per unit.g. Completed and transferred the standard cost associated with the 23,700 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.h. Paid $69,000 of selling and administrative expenses.i. Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.Required:1. Record the above transactions in the worksheet that appears below. The beginning balances have been provided for each of the accounts, including the Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) account which is abbreviated as PP&E (net).
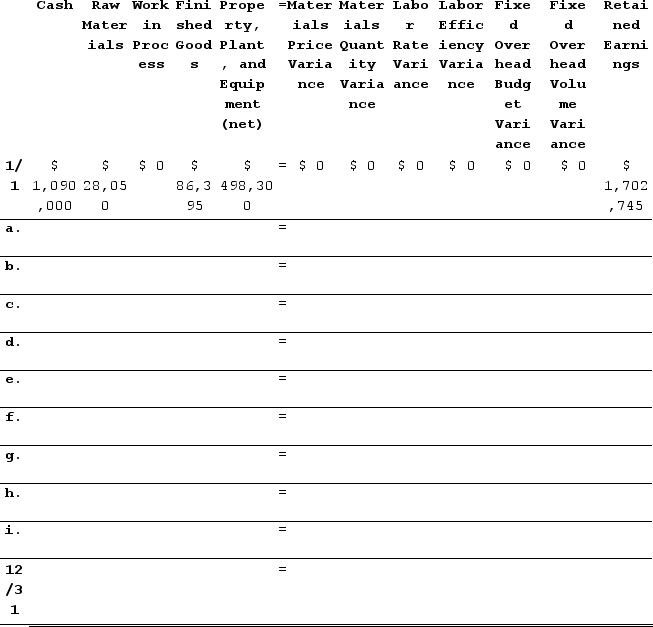 2.Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.
2.Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.
 The company calculated the following variances for the year:
The company calculated the following variances for the year: The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $48,750 and budgeted activity of 7,500 hours.
The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $48,750 and budgeted activity of 7,500 hours.During the year, the company completed the following transactions:
a. Purchased 45,600 gallons of raw material at a price of $4.90 per gallon.b. Used 40,220 gallons of the raw material to produce 23,600 units of work in process.c. Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 12,400 hours at an average cost of $21.70 per hour.d. Applied fixed overhead to the 23,600 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $34,050. Of this total, −$23,950 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $58,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment.e. Transferred 23,600 units from work in process to finished goods.f. Sold for cash 23,700 units to customers at a price of $27.20 per unit.g. Completed and transferred the standard cost associated with the 23,700 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.h. Paid $69,000 of selling and administrative expenses.i. Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.Required:1. Record the above transactions in the worksheet that appears below. The beginning balances have been provided for each of the accounts, including the Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) account which is abbreviated as PP&E (net).
 2.Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.
2.Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.On May 25, 2024
1. & 2.
 The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:a. Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Average price = 45,600 gallons × $4.90 per gallon = $223,440. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 45,600 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $250,800. The materials price variance is $27,360 Favorable.b. Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 40,220 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $221,210. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (23,600 units × 1.7 gallons per unit) × $5.50 per gallon = 40,120 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $220,660. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $550 Unfavorable.c. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,400 hours × $21.70 per hour = $269,080. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $21.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $21.50 per hour = $253,700. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $2,480 Unfavorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $12,900 Unfavorable.d. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is -$23,950. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $6.50 per hour = $76,700. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $58,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $14,700 Favorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $27,950 Favorable.e. Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 23,600 units × $23.35 per unit = $551,060. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.f. Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 23,700 units × $27.20 per unit = $644,640. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.g. Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 23,700 units × $23.35 per unit = $553,395. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.h. Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $69,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.i. All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).
The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:a. Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Average price = 45,600 gallons × $4.90 per gallon = $223,440. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 45,600 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $250,800. The materials price variance is $27,360 Favorable.b. Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 40,220 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $221,210. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (23,600 units × 1.7 gallons per unit) × $5.50 per gallon = 40,120 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $220,660. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $550 Unfavorable.c. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,400 hours × $21.70 per hour = $269,080. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $21.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $21.50 per hour = $253,700. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $2,480 Unfavorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $12,900 Unfavorable.d. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is -$23,950. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $6.50 per hour = $76,700. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $58,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $14,700 Favorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $27,950 Favorable.e. Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 23,600 units × $23.35 per unit = $551,060. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.f. Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 23,700 units × $27.20 per unit = $644,640. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.g. Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 23,700 units × $23.35 per unit = $553,395. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.h. Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $69,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.i. All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).
 The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:a. Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Average price = 45,600 gallons × $4.90 per gallon = $223,440. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 45,600 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $250,800. The materials price variance is $27,360 Favorable.b. Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 40,220 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $221,210. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (23,600 units × 1.7 gallons per unit) × $5.50 per gallon = 40,120 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $220,660. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $550 Unfavorable.c. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,400 hours × $21.70 per hour = $269,080. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $21.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $21.50 per hour = $253,700. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $2,480 Unfavorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $12,900 Unfavorable.d. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is -$23,950. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $6.50 per hour = $76,700. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $58,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $14,700 Favorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $27,950 Favorable.e. Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 23,600 units × $23.35 per unit = $551,060. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.f. Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 23,700 units × $27.20 per unit = $644,640. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.g. Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 23,700 units × $23.35 per unit = $553,395. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.h. Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $69,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.i. All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).
The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:a. Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Average price = 45,600 gallons × $4.90 per gallon = $223,440. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 45,600 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $250,800. The materials price variance is $27,360 Favorable.b. Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 40,220 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $221,210. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (23,600 units × 1.7 gallons per unit) × $5.50 per gallon = 40,120 gallons × $5.50 per gallon = $220,660. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $550 Unfavorable.c. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,400 hours × $21.70 per hour = $269,080. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $21.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $21.50 per hour = $253,700. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $2,480 Unfavorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $12,900 Unfavorable.d. Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is -$23,950. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (23,600 units × 0.50 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,800 hours × $6.50 per hour = $76,700. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $58,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $14,700 Favorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $27,950 Favorable.e. Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 23,600 units × $23.35 per unit = $551,060. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.f. Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 23,700 units × $27.20 per unit = $644,640. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.g. Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 23,700 units × $23.35 per unit = $553,395. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.h. Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $69,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.i. All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).MF
Answered
Financial engineering
A) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security.
B) primarily takes place for the institutional investor.
C) primarily takes places for the individual investor.
D) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security and primarily takes place for the institutional investor.
E) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security and primarily takes places for the individual investor.
A) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security.
B) primarily takes place for the institutional investor.
C) primarily takes places for the individual investor.
D) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security and primarily takes place for the institutional investor.
E) is the custom designing of securities or portfolios with desired patterns of exposure to the price of the underlying security and primarily takes places for the individual investor.
On May 22, 2024
D