Asked by Alivia Thomas on May 06, 2024

Verified
Using the following information, calculate the z-statistic for the z-test for one mean. 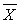 = 15 μ = 22
= 15 μ = 22 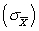 = 3.50
= 3.50
A) 2.00
B) -2.00
C) 1.23
D) -3.13
Z-statistic
A type of standard score that indicates how many standard deviations an element is from the mean of its distribution.
Z-test
A statistical test used to determine whether there is a significant difference between the mean of a sample and the population mean, assuming the distribution is normal.
µ = 22
Represents a population mean of 22 in statistical notation.
- Evaluate the z-statistics for chosen datasets.

Verified Answer
z = (x̄ - μ) / (σ / √n)
where x̄ is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, σ is the population standard deviation, and n is the sample size.
From the given information, we have:
x̄ = 15
μ = 22
σ is unknown
n = 3.50
Since we do not have the population standard deviation, we cannot calculate the z-statistic directly. Therefore, we need to use a t-test with degrees of freedom (df) = n - 1 = 2.
The t-statistic can be calculated as:
t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n)
where s is the sample standard deviation.
From the given information, we have:
s = 3.50
Therefore,
t = (15 - 22) / (3.50 / √3) = -3.13
Using a t-distribution table with df = 2, we find that the two-tailed critical value at α = 0.05 is approximately 4.303.
Since the calculated t-value (-3.13) is less than the critical value (-4.303), we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the sample mean is significantly different from the population mean at α = 0.05.
To convert this result to a z-statistic, we can use the relationship between t and z:
z = t / √df
Substituting the values, we get:
z = -3.13 / √2 = -2.22
Therefore, the z-statistic for the z-test for one mean is -2.22, which is closest to choice B (-2.00).

Learning Objectives
- Evaluate the z-statistics for chosen datasets.
Related questions
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Calvin Is Graduating and Wants to Get a Job in ...
The Results of a Recent Survey Showed That the Average ...