Asked by Hannah McCoy on May 03, 2024

Verified
Using the following information, calculate the z-statistic for the z-test for one mean. 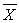 = 27 μ = 15
= 27 μ = 15 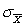 = 1.50
= 1.50
A) -8.00
B) 8.00
C) 4.00
D) -.10
Z-test
A statistical test used to determine whether two population means are different when the variances are known and the sample size is large.
µ = 15
Represents the mean of a population is equal to 15.
- Calculate z-statistics for given datasets.

Verified Answer
KS
Kelsey SpradleyMay 08, 2024
Final Answer :
B
Explanation :
To calculate the z-statistic, we use the formula: z = (x - μ) / (σ / sqrt(n)), where x is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, σ is the population standard deviation, and n is the sample size.
In this case, we are given x = 27, μ = 15, and σ = 1.50. We are not given the sample size, so we cannot calculate the standard error directly.
However, if we assume that the sample size is large enough (i.e. n > 30), we can use the central limit theorem and approximate the distribution of sample means to a normal distribution with a standard error of σ / sqrt(n).
Assuming a large enough sample size, the z-statistic is:
z = (27 - 15) / (1.5 / sqrt(n))
z = 12 / (1.5 / sqrt(n))
z = 8 * sqrt(n)
Since we do not know n, we cannot calculate the exact value of the z-statistic. However, we can see that the z-statistic is positive and large, which indicates that the sample mean is significantly higher than the population mean. Therefore, the best choice is B, 8.00.
In this case, we are given x = 27, μ = 15, and σ = 1.50. We are not given the sample size, so we cannot calculate the standard error directly.
However, if we assume that the sample size is large enough (i.e. n > 30), we can use the central limit theorem and approximate the distribution of sample means to a normal distribution with a standard error of σ / sqrt(n).
Assuming a large enough sample size, the z-statistic is:
z = (27 - 15) / (1.5 / sqrt(n))
z = 12 / (1.5 / sqrt(n))
z = 8 * sqrt(n)
Since we do not know n, we cannot calculate the exact value of the z-statistic. However, we can see that the z-statistic is positive and large, which indicates that the sample mean is significantly higher than the population mean. Therefore, the best choice is B, 8.00.

Learning Objectives
- Calculate z-statistics for given datasets.
Related questions
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Using the Following Information, Calculate the Z-Statistic for the Z-Test ...
Calvin Is Graduating and Wants to Get a Job in ...
The Results of a Recent Survey Showed That the Average ...