Asked by Patrick Ritchie on Jul 06, 2024

Verified
Write, in factored form, an expression for the area of the constructed figure below if A is unknown and B is equal to 666 . 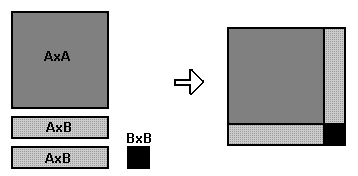
A) A(A+6) A ( A + 6 ) A(A+6)
B) (A−6) 2( A - 6 ) ^ { 2 }(A−6) 2
C) (A+6) 2( A + 6 ) ^ { 2 }(A+6) 2
D) (A+6) (A−6) ( A + 6 ) ( A - 6 ) (A+6) (A−6)
E) A(A−6) A ( A - 6 ) A(A−6)
Factored Form
An expression represented as the product of its factors.
Constructed Figure
A geometric shape that is drawn or created using specific rules or tools.
- Use factoring to solve real-world problems and construct mathematical models.

Verified Answer
RR
Rahul RadheshJul 13, 2024
Final Answer :
C
Explanation :
The constructed figure is a rectangle with one side of length A and the other side of length B, which is known to be 6. Therefore, the area of the rectangle is A times 6, or 6A. However, the figure also has two identical quarter-circles with radius B = 6, which add to the rectangle to form the full figure. The area of each quarter-circle is (1/4) times pi times the radius squared, or (1/4) times pi times 6 squared, which simplifies to 9pi. Therefore, the total area of the figure is the area of the rectangle, 6A, plus the combined area of the two quarter-circles, which is 2 times 9pi, or 18pi. Factoring out 6 from 6A gives 6(A), and factoring out 9pi from 18pi gives 9pi(2). Therefore, the total area can be expressed as 6A + 9pi(2), or in factored form as (A + 6)(A + 6), which simplifies to (A + 6)². Therefore, the best choice is C, (A+6)2( A + 6 ) ^ { 2 }(A+6)2 .

Learning Objectives
- Use factoring to solve real-world problems and construct mathematical models.