JM
Jayleen Marie
Answers (13)
JM
Answered
What reactive intermediate is formed when CHBr3 is treated with hydroxide or when diazomethane is irradiated?
A) carbene
B) carbanion
C) carbocation
D) carbon radical
A) carbene
B) carbanion
C) carbocation
D) carbon radical
On Aug 04, 2024
A
JM
Answered
What is the [H+] concentration of a solution with pH = 8?
A) 1 × 10-8
B) 1 × 108
C) 1.8 × 10-8
D) 8.1 × 10+8
A) 1 × 10-8
B) 1 × 108
C) 1.8 × 10-8
D) 8.1 × 10+8
On Jul 12, 2024
A
JM
Answered
What formula does an ionic compound made from aluminum and chlorine have?
A) AlCl2
B) AlCl3
C) Al2Cl
D) Al3Cl
A) AlCl2
B) AlCl3
C) Al2Cl
D) Al3Cl
On Jul 07, 2024
B
JM
Answered
What does aerobic respiration of glucose produce in the first step?
A) Lactic acid
B) Lactate
C) Pyruvate
D) Gluconate
A) Lactic acid
B) Lactate
C) Pyruvate
D) Gluconate
On Jun 11, 2024
C
JM
Answered
Provide the structure of the major organic product that results when 4-methyl-1-pentanol is treated with PBr3.
On Jun 06, 2024
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH2Br
JM
Answered
Which of the presented mechanisms would be the most energetically favorable and thus the most likely mechanism to actually occur for the following free radical chain reaction?
(bond dissociation energies - H-H = 104 kcal/mol; Cl-Cl = 58 kcal/mol; H-Cl = 103 kcal/mol)
H2 + Cl2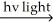 2 HCl
2 HCl
A) H2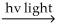 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙
H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
B) Cl2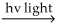 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl2 → HCl + Cl∙
C) H2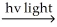 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙
H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
Cl∙ + H2 → HCl + H∙
D) Cl2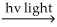 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
(bond dissociation energies - H-H = 104 kcal/mol; Cl-Cl = 58 kcal/mol; H-Cl = 103 kcal/mol)
H2 + Cl2
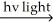 2 HCl
2 HClA) H2
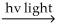 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
B) Cl2
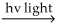 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl2 → HCl + Cl∙
C) H2
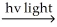 H∙ + H∙
H∙ + H∙H∙ + Cl2 → Cl∙ + HCl
Cl∙ + H2 → HCl + H∙
D) Cl2
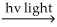 Cl∙ + Cl∙
Cl∙ + Cl∙Cl∙ + H2 → H∙ + HCl
H∙ + Cl∙ → HCl
On May 28, 2024
B
JM
Answered
How does the oxidation number of O change in the following reaction:
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 → 4 CO2 + 6 H2O?
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 → 4 CO2 + 6 H2O?
On May 18, 2024
It changes from 0 to -2.
JM
Answered
What is given off in any reaction that is classified as an explosion?
A) Noise and light
B) Gaseous chemical products and energy
C) Heat and smoke
D) Gaseous chemical products and smoke
A) Noise and light
B) Gaseous chemical products and energy
C) Heat and smoke
D) Gaseous chemical products and smoke
On May 12, 2024
B
JM
Answered
________ polymers result from rapid reaction of one molecule at a time with a growing polymer chain, usually with a reactive intermediate at the growing end of the chain.
A) Addition
B) Condensation
C) Step-growth
D) Amorphous
A) Addition
B) Condensation
C) Step-growth
D) Amorphous
On May 02, 2024
A