JS
Joshua Sanchez
Answers (4)
JS
Answered
Prepaid expenses,depreciation,accrued expenses,unearned revenues,and accrued revenues are all examples of:
A) Items that require contra accounts.
B) Items that require adjusting entries.
C) Asset and equity accounts.
D) Asset accounts.
E) Income statement accounts.
A) Items that require contra accounts.
B) Items that require adjusting entries.
C) Asset and equity accounts.
D) Asset accounts.
E) Income statement accounts.
On Jun 21, 2024
B
JS
Answered
An increase in unemployment benefits is likely to:
A) reduce a person's incentive to look for work.
B) reduce the opportunity cost of remaining employed.
C) provide a better safety net for employed families.
D) decrease the tax imposed on consumers.
E) increase the need to accept the first job available after becoming unemployed.
A) reduce a person's incentive to look for work.
B) reduce the opportunity cost of remaining employed.
C) provide a better safety net for employed families.
D) decrease the tax imposed on consumers.
E) increase the need to accept the first job available after becoming unemployed.
On Jun 19, 2024
A
JS
Answered
In the dividend discount model, which of the following are not incorporated into the discount rate?
A) Real risk-free rate
B) Risk premium for stocks
C) Return on assets
D) Expected inflation rate
A) Real risk-free rate
B) Risk premium for stocks
C) Return on assets
D) Expected inflation rate
On May 22, 2024
C
JS
Answered
Kropf Incorporated has provided the following data concerning one of the products in its standard cost system. Variable manufacturing overhead is applied to products on the basis of direct labor-hours.
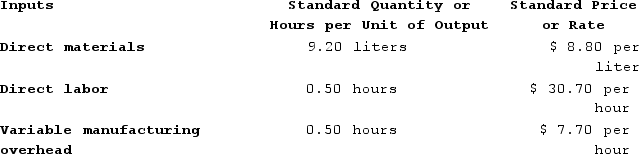 The company has reported the following actual results for the product for September:
The company has reported the following actual results for the product for September:
 Required:a. Compute the materials price variance for September.b. Compute the materials quantity variance for September.c. Compute the labor rate variance for September.d. Compute the labor efficiency variance for September.e. Compute the variable overhead rate variance for September.f. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance for September.
Required:a. Compute the materials price variance for September.b. Compute the materials quantity variance for September.c. Compute the labor rate variance for September.d. Compute the labor efficiency variance for September.e. Compute the variable overhead rate variance for September.f. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance for September.
 The company has reported the following actual results for the product for September:
The company has reported the following actual results for the product for September: Required:a. Compute the materials price variance for September.b. Compute the materials quantity variance for September.c. Compute the labor rate variance for September.d. Compute the labor efficiency variance for September.e. Compute the variable overhead rate variance for September.f. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance for September.
Required:a. Compute the materials price variance for September.b. Compute the materials quantity variance for September.c. Compute the labor rate variance for September.d. Compute the labor efficiency variance for September.e. Compute the variable overhead rate variance for September.f. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance for September.On May 20, 2024
a.Materials price variance = (Actual quantity × Actual price) − (Actual quantity × Standard price)= ${{[a(9)]:#,###}} − ({{[a(8)]:#,###}} liters × ${{[a(4)]:#,###}} per liter)= ${{[a(9)]:#,###}} − ${{[a(14)]:#,###}}= ${{[a(21)]:#,###}} Unfavorableb.Standard quantity = {{[a(7)]:#,###}} units × {{[a(1)]:#,###.0}} liters per unit = {{[a(15)]:#,###}} litersMaterials quantity variance = (Actual quantity × Standard price) − (Standard quantity × Standard price)= (Actual quantity − Standard quantity) × Standard price= ({{[a(10)]:#,###}} liters − {{[a(15)]:#,###}} liters) × ${{[a(4)]:#,###.00}} per liter= {{[a(16)]:#,###}} liters × ${{[a(4)]:#,###.00}} per liter= ${{[a(22)]:#,###}} Unfavorablec.Labor rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)= ${{[a(12)]:#,###}} − ({{[a(11)]:#,###}} hours × ${{[a(5)]:#,###.0}} per hour)= ${{[a(12)]:#,###}} − ${{[a(17)]:#,###}}= ${{[a(23)]:#,###}} Unfavorabled.Standard hours = {{[a(7)]:#,###}} units × {{[a(2)]:#,##0.00}} hours per unit = {{[a(18)]:#,###}} hoursLabor efficiency variance = (Actual hours × Standard rate) − (Standard hours × Standard rate)= (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate= ({{[a(11)]:#,###}} hours − {{[a(18)]:#,###}} hours) × ${{[a(5)]:#,###.00}} per hour= (−{{[a(19)]:#,###}} hours) × ${{[a(5)]:#,###.00}} per hour= ${{[a(24)]:#,###}} Favorablee.Variable overhead rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)= ${{[a(13)]:#,###}} − ({{[a(11)]:#,###}} hours × ${{[a(6)]:#,###}} per hour)= ${{[a(13)]:#,###}} − (${{[a(20)]:#,###}})= ${{[a(25)]:#,###}} Favorablef.Standard hours = {{[a(7)]:#,###}} units × {{[a(2)]:#,##0.00}} hours per unit = {{[a(18)]:#,###}} hoursVariable overhead efficiency variance = (Actual hours × Standard rate) − (Standard hours × Standard rate)= (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate= ({{[a(11)]:#,###}} hours − {{[a(18)]:#,###}} hours) × ${{[a(6)]:#,###}} per hour= (−{{[a(19)]:#,###}} hours) × ${{[a(6)]:#,###.00}} per hour = ${{[a(26)]:#,###}} Favorable