LT
Lamar Tossils
Answers (6)
LT
Answered
If relevant events are _____,diversification will NOT reduce risk.
A) positively correlated
B) negatively correlated
C) dependent
D) independent
A) positively correlated
B) negatively correlated
C) dependent
D) independent
On Jul 25, 2024
A
LT
Answered
The direct materials quantity standard would not be expressed in
A) pounds.
B) barrels.
C) dollars.
D) board feet.
A) pounds.
B) barrels.
C) dollars.
D) board feet.
On Jul 22, 2024
C
LT
Answered
Traditionally, crisis management was viewed negatively as
A) an executive reality check.
B) business as usual.
C) managerial firefighting.
D) concurrent control.
E) a variable cost.
A) an executive reality check.
B) business as usual.
C) managerial firefighting.
D) concurrent control.
E) a variable cost.
On Jun 25, 2024
C
LT
Answered
Juliani Company produces a single product.The cost of producing and selling a single unit of this product at the company's normal activity level of 50,000 units per month is as follows: 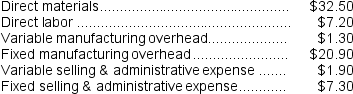 The normal selling price of the product is $75.00 per unit.
The normal selling price of the product is $75.00 per unit.
An order has been received from an overseas customer for 3,000 units to be delivered this month at a special discounted price.This order would have no effect on the company's normal sales and would not change the total amount of the company's fixed costs.The variable selling and administrative expense would be $0.30 less per unit on this order than on normal sales.
Direct labor is a variable cost in this company.
Required:
a.Suppose there is ample idle capacity to produce the units required by the overseas customer and the special discounted price on the special order is $65.60 per unit.What is the financial advantage (disadvantage)for the company next month if it accepts the special order?
b.Suppose the company is already operating at capacity when the special order is received from the overseas customer.What would be the opportunity cost of each unit delivered to the overseas customer?
c.Suppose there is not enough idle capacity to produce all of the units for the overseas customer and accepting the special order would require cutting back on production of 1,000 units for regular customers.What would be the minimum acceptable price per unit for the special order?
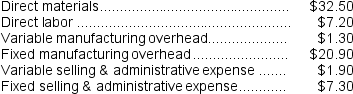 The normal selling price of the product is $75.00 per unit.
The normal selling price of the product is $75.00 per unit.An order has been received from an overseas customer for 3,000 units to be delivered this month at a special discounted price.This order would have no effect on the company's normal sales and would not change the total amount of the company's fixed costs.The variable selling and administrative expense would be $0.30 less per unit on this order than on normal sales.
Direct labor is a variable cost in this company.
Required:
a.Suppose there is ample idle capacity to produce the units required by the overseas customer and the special discounted price on the special order is $65.60 per unit.What is the financial advantage (disadvantage)for the company next month if it accepts the special order?
b.Suppose the company is already operating at capacity when the special order is received from the overseas customer.What would be the opportunity cost of each unit delivered to the overseas customer?
c.Suppose there is not enough idle capacity to produce all of the units for the overseas customer and accepting the special order would require cutting back on production of 1,000 units for regular customers.What would be the minimum acceptable price per unit for the special order?
On Jun 22, 2024
a.
Variable cost per unit on normal sales: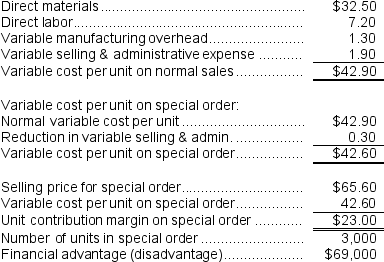 b.The opportunity cost is just the contribution margin on normal sales:
b.The opportunity cost is just the contribution margin on normal sales:  c.Minimum acceptable price:
c.Minimum acceptable price: 
Variable cost per unit on normal sales:
 b.The opportunity cost is just the contribution margin on normal sales:
b.The opportunity cost is just the contribution margin on normal sales:  c.Minimum acceptable price:
c.Minimum acceptable price: 
LT
Answered
Bridget's Brewery production function is given by 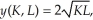 where K is the number of vats she uses and L is the number of labor hours. Does this production process exhibit increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale? Holding the number of vats constant at 4, is the marginal product of labor increasing, constant or decreasing as more labor is used?
where K is the number of vats she uses and L is the number of labor hours. Does this production process exhibit increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale? Holding the number of vats constant at 4, is the marginal product of labor increasing, constant or decreasing as more labor is used?
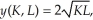 where K is the number of vats she uses and L is the number of labor hours. Does this production process exhibit increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale? Holding the number of vats constant at 4, is the marginal product of labor increasing, constant or decreasing as more labor is used?
where K is the number of vats she uses and L is the number of labor hours. Does this production process exhibit increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale? Holding the number of vats constant at 4, is the marginal product of labor increasing, constant or decreasing as more labor is used?On May 26, 2024
Since 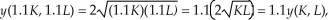 we know the production process exhibits constant returns to scale. Holding the number of vats constant at 4 will still result in a downward sloping marginal product of labor curve. That is the marginal product of labor decreases as more labor is used.
we know the production process exhibits constant returns to scale. Holding the number of vats constant at 4 will still result in a downward sloping marginal product of labor curve. That is the marginal product of labor decreases as more labor is used.
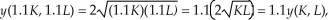 we know the production process exhibits constant returns to scale. Holding the number of vats constant at 4 will still result in a downward sloping marginal product of labor curve. That is the marginal product of labor decreases as more labor is used.
we know the production process exhibits constant returns to scale. Holding the number of vats constant at 4 will still result in a downward sloping marginal product of labor curve. That is the marginal product of labor decreases as more labor is used.LT
Answered
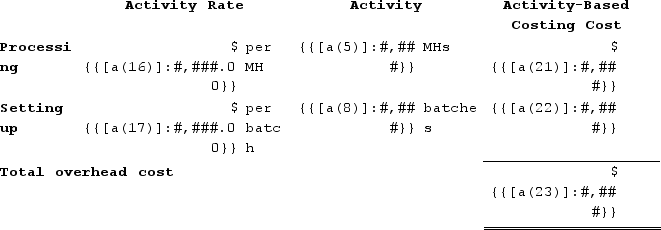
Zwahlen Corporation has an activity-based costing system with three activity cost pools--Processing, Setting Up, and Other. Costs in the Processing cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products. Data concerning the two products and the company's costs and activity-based costing system appear below:Activity Cost Pools
 Required:a. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) b. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) c. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Required:a. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) b. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) c. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
 Required:a. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) b. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) c. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Required:a. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) b. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) c. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)On May 23, 2024
a. Computation of activity rates:
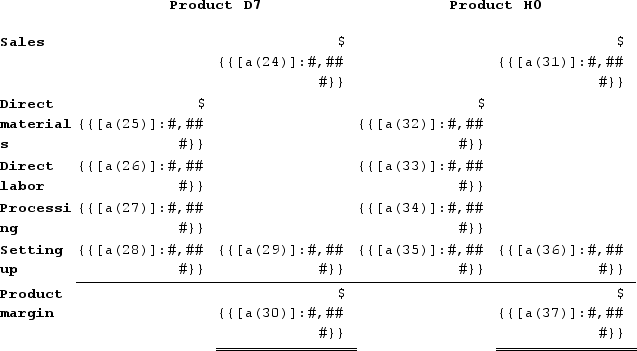
 b. The overhead cost charged to Product D7 is:
b. The overhead cost charged to Product D7 is:
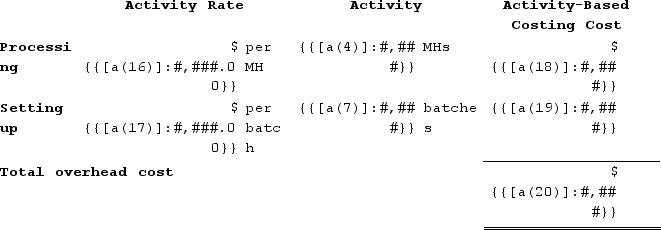 The overhead cost charged to Product H0 is:
The overhead cost charged to Product H0 is:
 c. Determine product margins:
c. Determine product margins:
 b. The overhead cost charged to Product D7 is:
b. The overhead cost charged to Product D7 is: The overhead cost charged to Product H0 is:
The overhead cost charged to Product H0 is: c. Determine product margins:
c. Determine product margins: