TT
tolaa touch
Answers (6)
TT
Answered
The single most important criterion for selecting an investor is the size of fund it can provide to an organization.
On Jul 27, 2024
False
TT
Answered
If you pay a $2,000 tax on $10,000 of taxable income and a $4,000 tax on a taxable income of $16,000, the tax is progressive.
On Jul 24, 2024
True
TT
Answered
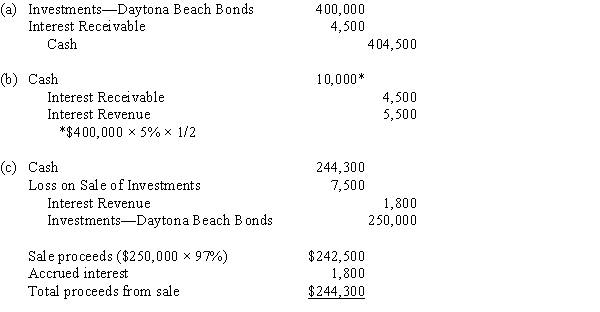
Journalize the entries to record the following selected bond investment transactions for Southwest Bank:
(a)Purchased $400,000 of Daytona Beach 5% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $4,500.(b)Received the first semiannual interest.(c)Sold $250,000 of the bonds at 97, plus accrued interest of $1,800.
(a)Purchased $400,000 of Daytona Beach 5% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $4,500.(b)Received the first semiannual interest.(c)Sold $250,000 of the bonds at 97, plus accrued interest of $1,800.
On Jun 27, 2024
TT
Answered
Flyer Corporation manufactures two products, Product A and Product B.Product B is of fairly recent origin, having been developed as an attempt to enter a market closely related to that of Product A.Product B is the more complex of the two products, requiring three hours of direct labor time per unit to manufacture compared to one and one-half hours of direct labor time for Product A.Product B is produced on an automated production line.
Overhead is currently assigned to the products on the basis of direct-labor-hours.The company estimated it would incur $396,000 in manufacturing overhead costs and produce 5,500 units of Product B and 22,000 units of Product A during the current year.Unit costs for materials and direct labor are: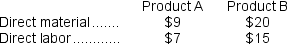 Required:
Required:
a.Compute the predetermined overhead rate under the current method of allocation and determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
b.The company's overhead costs can be attributed to four major activities.These activities and the amount of overhead cost attributable to each for the current year are given below: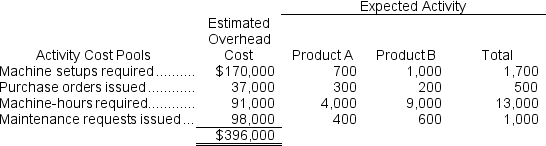 Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Overhead is currently assigned to the products on the basis of direct-labor-hours.The company estimated it would incur $396,000 in manufacturing overhead costs and produce 5,500 units of Product B and 22,000 units of Product A during the current year.Unit costs for materials and direct labor are:
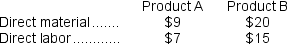 Required:
Required:a.Compute the predetermined overhead rate under the current method of allocation and determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
b.The company's overhead costs can be attributed to four major activities.These activities and the amount of overhead cost attributable to each for the current year are given below:
 Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.On Jun 24, 2024
a.The company expects to work 45,000 direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows:  Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:
Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:
Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = $396,000 ÷ 49,500 DLHs = $8.00 per DLH
Using this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: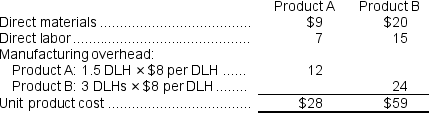 b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:
b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: 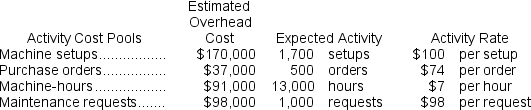 The overhead cost charged to each product is:
The overhead cost charged to each product is:
The overhead cost charged to Product A is: Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)
The overhead cost charged to Product B is: Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)
Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be: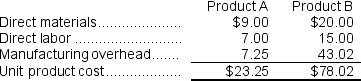
 Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:
Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = $396,000 ÷ 49,500 DLHs = $8.00 per DLH
Using this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be:
 b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:
b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:  The overhead cost charged to each product is:
The overhead cost charged to each product is:The overhead cost charged to Product A is:
 Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product B is:
 Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:

TT
Answered
Costs of the firm that rise with increased levels of investment in its current assets are called:
A) Carrying costs.
B) Shortage costs.
C) Order costs.
D) Safety costs.
E) Trading costs.
A) Carrying costs.
B) Shortage costs.
C) Order costs.
D) Safety costs.
E) Trading costs.
On May 28, 2024
A
TT
Answered
Describe the flow of materials in a process cost accounting system.
On May 25, 2024
When raw materials are purchased, they are debited to Materials. When direct materials are needed in a production department, a materials requisition report is used to move the materials from the storeroom to the production department. Direct materials used are recorded with a debit to Work in Process Inventory for that department and a credit to Materials. Indirect materials used in a department are recorded with a debit to Factory Overhead and a credit to Materials.